- What is UV radiation?
- How is radiation classified on the electromagnetic spectrum?
- What are the different types of UV radiation?
- What Is UVC radiation?
- What are the risks of exposure to UVC radiation?
- What are the risks associated with using some UVC lamps?
- What effect does UV radiation have on my body?
- Are there health benefits of exposure to UV radiation?
- Does where I live affect the amount of UV radiation I am exposed to?
- What is the UV Index (UVI)?
Q: What is UV Radiation?
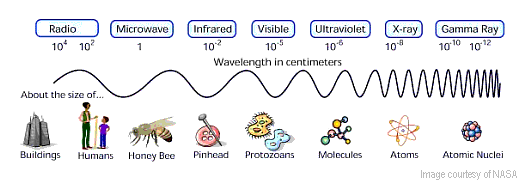
All radiation is a form of energy, most of which is invisible to the human eye. UV radiation is only one form of radiation and it is measured on a scientific scale called the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum.
UV radiation is only one type of EM energy you may be familiar with. Radio waves that transmit sound from a radio station’s tower to your stereo, or between cell phones; microwaves, like those that heat your food in a microwave oven; visible light that is emitted from the lights in your home; and X-rays like those used in hospital X-ray machines to capture images of the bones inside your body, are all forms of EM energy.
UV radiation is the portion of the EM spectrum between X-rays and visible light.
More Information on UV Radiation
Q: How is radiation classified on the electromagnetic spectrum?
Electromagnetic radiation is all around us, though we can only see some of it. All EM radiation (also called EM energy) is made up of minute packets of energy or 'particles,' called photons, which travel in a wave-like pattern and move at the speed of light. The EM spectrum is divided into categories defined by a range of numbers. These ranges describe the activity level, or how energetic the photons are, and the size of the wavelength in each category.
For example, at the bottom of the spectrum radio waves have photons with low energies, so their wavelengths are long with peaks that are far apart. The photons of microwaves have higher energies, followed by infrared waves, UV rays, and X-rays. At the top of the spectrum, gamma rays have photons with very high energies and short wavelengths with peaks that are close together.
More Information on the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Q: What are the different types of UV radiation?
The most common form of UV radiation is sunlight, which produces three main types of UV rays:
- UVA
- UVB
- UVC
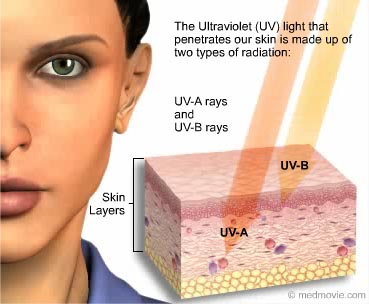
UVA rays have the longest wavelengths, followed by UVB, and UVC rays which have the shortest wavelengths. While UVA and UVB rays are transmitted through the atmosphere, all UVC and some UVB rays are absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer. So, most of the UV rays you come in contact with are UVA with a small amount of UVB.
Like all forms of light on the EM spectrum, UV radiation is classified by wavelength. Wavelength describes the distance between the peaks in a series of waves.
- UVB rays have a short wavelength that reaches the outer layer of your skin (the epidermis)
- UVA rays have a longer wavelength that can penetrate the middle layer of your skin (the dermis)
Q: What is UVC Radiation?
A: UVC radiation is the highest energy portion of the UV radiation spectrum.
UVC radiation from the sun does not reach the earth’s surface because it is blocked by the ozone layer in the atmosphere. Thus, the only way that humans can be exposed to UVC radiation is from an artificial source like a lamp or laser.
Q: What are the risks of exposure to UVC radiation?
A: UVC radiation can cause severe burns of the skin and eye injuries (photokeratitis). Avoid direct skin exposure to UVC radiation and never look directly into a UVC light source, even briefly. Skin burns and eye injuries from UVC exposure usually resolve within a week with no known long-term damage. Since the penetration depth of UVC radiation is very low, the risk of skin cancer, cataracts or permanent vision loss is also thought to be very low. The type of eye injury associated with exposure to UVC causes severe pain and a feeling of having sand in the eyes. Sometimes people are unable to use their eyes for one to two days. It can occur after a very short exposure (seconds to minutes) to UVC radiation.
If you have experienced an injury associated with using a UVC lamp, we encourage you to report it to the FDA.
Q: What are the risks associated with using some UVC lamps?
A: Some UVC lamps emit small amounts of UVB radiation. Therefore, exposure to a high dose or prolonged low dose of radiation from some UVC lamps can potentially contribute to effects like cataracts or skin cancer that are caused by cumulative exposure to UVB radiation.
Additionally, some UVC lamps generate ozone which could cause irritation to breathing passages (that is nose, throat, and lungs), particularly for those who have respiratory sensitivity such as asthma or allergies. Exposure to high levels of ozone gas may also worsen chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma, or increase vulnerability to respiratory infection.
Q: What effect does UV radiation have on my body?
Both UVA and UVB rays can cause damage to your skin. Sunburn is a sign of short-term overexposure, while premature aging and skin cancer are side effects of prolonged UV exposure.
Certain oral and topical medicines, such as antibiotics, birth control pills, and benzoyl peroxide products, as well as some cosmetics, may increase skin and eye sensitivity to UV in all skin types. Check the label and ask your doctor for more information.
Sunlight is not the only source of UV radiation you may encounter. Other sources include:
- Tanning booths
- Mercury vapor lighting (often found in stadiums and school gyms)
- Some halogen, fluorescent, and incandescent lights
- Some types of lasers
More information on the Risks of Tanning
More Information on the Known Health Effects of UV
More Information on Health Effects of Overexposure to the Sun
More Information on the Types of UV Radiation
Q: Are there health benefits of exposure to UV radiation?
Exposure to UVB radiation helps the skin produce a type of vitamin D, (vitamin D3), which plays an important role - along with calcium - in bone and muscle health. However, the amount of UVB exposure needed to obtain a benefit depends on several factors, such as: the amount of vitamin D in your diet, skin color, sunscreen use, clothing, where you live (latitude and altitude), time of day, and time of year. Also, the FDA has not cleared or approved any indoor tanning device for producing Vitamin D.
UV radiation, in the form of lasers, lamps, or a combination of these devices and topical medications that increase UV sensitivity, are sometimes used to treat patients with certain diseases who have not responded to other methods of therapy. Also known as phototherapy, this method of UV exposure is performed by a trained healthcare professional under the supervision of a dermatologist. Studies suggest that phototherapy can help treat unresponsive and severe cases of several diseases, including:
Phototherapy involves exposing a patient to a carefully monitored dose of UV radiation on a regular schedule. In some cases, effective therapy requires that a patient’s skin is first treated with a prescription drug, ointment, or bath that increases its UV sensitivity. While this type of therapy does not eliminate the negative side-effects of UV exposure, treatment is carefully supervised by a doctor to ensure that the benefits outweigh the risks.
Q: Does where I live affect the amount of UV radiation I am exposed to?
Many factors determine how much UV you are exposed to, including:
- Geography
- Altitude
- Time of year
- Time of day
- Weather conditions
- Reflection
Geography
UV rays are strongest in areas close to the equator. Because the sun is directly over the equator, UV rays only travel a short distance through the atmosphere to reach these areas. UV radiation is also the strongest near the equator because ozone in these areas is naturally thinner, so there is less to absorb the UV radiation.
UV exposure is lower in areas further from the equator because the sun is farther away. Exposure is also decreased because UV rays must travel a greater distance through ozone-rich portions of the atmosphere to reach the earth’s surface.
UV exposure is also greater in areas of snow, sand, pavement, and water due to the reflective properties of these surfaces.
Altitude
Altitude is another contributing factor to the amount of UV. Higher altitudes have greater UV exposure because there is less atmosphere to absorb UV rays.
Time of Year
The sun’s angle in relation to the Earth varies according to season. During the summer months the sun is in a more direct angle, resulting in a greater amount of UV radiation.
Time of Day
UV is most intense at noon when the sun is at its highest point in the sky, and UV rays have the least distance to travel through the atmosphere. Especially in the hot summer months, it is a good idea to remain indoors during the peak sun hours of 10am and 4pm.
Weather Conditions
Many people believe that you cannot get sunburned on a cloudy day; this is simply not the case. Even under cloud cover it is possible to damage your skin and eyes, and cause long-term damage. It is important that you protect yourself with sunscreen, even in cloudy weather.
Reflection
Some surfaces, such as snow, sand, grass, or water can reflect much of the UV radiation that reaches them. Sunglasses rated for 100% UV protection, a wide-brim hat, and broad-spectrum sunscreen can help protect your eyes and skin from reflected UV rays.
More Information on Environmental Factors of UV Exposure
Q: What is the UV Index (UVI)?
The Ultraviolet Index (UVI) is a rating scale, with numbers from 1 to 11, which indicate the amount of skin-damaging UV rays reaching the Earth’s surface during the day.
The daily UVI forecasts the amount of UV reaching your area at noon when the sun typically reaches its highest point in the sky. The higher the UVI number, the more intense the UV rays you will be exposed to.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) offers UVI forecasts by ZIP code on their UV Index page.
Many illustrations of the UVI use a system of colors to designate levels of UV exposure for a particular area on the map. The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed an internationally recognized system of colors corresponding to levels of the UVI.
| Category | UVI Range | Color |
|---|---|---|
| Low | 0 – 2 | Green |
| Moderate | 3 – 5 | Yellow |
| High | 6 – 7 | Orange |
| Very High | 8 – 10 | Red |
| Extreme | 11 + | Purple |
I am an expert in the field of UV radiation and its effects on the human body. My knowledge is grounded in both theoretical understanding and practical experience, having extensively researched and worked in areas related to electromagnetic radiation, UV radiation, and its impact on health. My expertise is supported by a comprehensive understanding of the scientific principles underpinning radiation, as well as a keen awareness of real-world applications and implications.
Now, let's delve into the concepts covered in the article:
UV Radiation and Electromagnetic Spectrum
UV radiation is a form of energy within the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. This spectrum encompasses various types of energy, ranging from radio waves to X-rays. UV radiation falls between X-rays and visible light on the spectrum. The spectrum is categorized by the energy levels and wavelengths of photons, with shorter wavelengths indicating higher energy.
Types of UV Radiation
There are three main types of UV radiation produced by the sun: UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA has the longest wavelength, UVB has a shorter wavelength that reaches the skin's outer layer, and UVC has the shortest wavelength. UVC radiation is particularly high-energy but is blocked by the Earth's ozone layer, so exposure primarily occurs through artificial sources like lamps or lasers.
Risks of UVC Radiation Exposure
Exposure to UVC radiation can cause severe burns to the skin and eye injuries (photokeratitis). Although the penetration depth is low, prolonged exposure may contribute to effects like cataracts or skin cancer. Some UVC lamps also emit small amounts of UVB radiation and may generate ozone, leading to potential health risks, especially for individuals with respiratory sensitivity.
Effects of UV Radiation on the Body
Both UVA and UVB rays can damage the skin, causing sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Certain medications and cosmetics may increase sensitivity to UV radiation. UV exposure is not limited to sunlight and can occur through various sources like tanning booths, certain lights, and lasers.
Health Benefits of UV Radiation
Exposure to UVB radiation aids in the production of vitamin D, essential for bone and muscle health. Controlled UV exposure, through methods like phototherapy, is used to treat certain diseases such as psoriasis and vitiligo. However, these treatments are supervised by healthcare professionals to balance the benefits and risks.
Factors Affecting UV Exposure
Various factors influence the amount of UV exposure, including geography, altitude, time of year, time of day, weather conditions, and reflection. UV rays are strongest near the equator, at higher altitudes, during the summer, and at midday. Surfaces like snow and water can reflect UV radiation, increasing exposure.
UV Index (UVI)
The UV Index (UVI) is a rating scale indicating the amount of skin-damaging UV rays reaching the Earth's surface. It ranges from 1 to 11, with higher numbers representing more intense UV rays. The UVI is categorized into colors, each corresponding to a level of UV exposure, from green (low) to purple (extreme).
In summary, understanding UV radiation involves knowledge of its classification in the electromagnetic spectrum, the types of UV rays, associated risks, effects on the body, potential benefits, and factors influencing exposure. Monitoring UV levels through the UV Index is crucial for adopting protective measures against excessive UV exposure.